OBJECT RECOGNITION – 21096
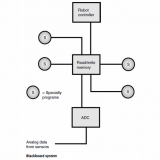
Object recognition refers to any method that a robot uses to pick something out from among other things. An example is getting a tumbler from a cupboard. It might require that the robot choose a specific object, such as “Jane’s tumbler.”
Suppose you ask your personal robot to go to the kitchen and get you a tumbler full of orange juice. The first thing the robot must do is find the kitchen. Then it must locate the cupboard containing the tumblers. How will the robot pick a tumbler, and not a plate or a bowl, from the cupboard? This is a form of bin picking problem.
One way for the robot to find a tumbler is with a vision systemto identify it by shape.Another method is tactile sensing. The robot can double-check, after grabbing an object it thinks is a tumbler, to see whether it is cylindrical (the characteristic shape of a tumbler). If all the tumblers in your cupboard weigh the same, and if this weight is different from that of the plates or bowls, the robot can use weight to double-check that it has the right object. If a particular tumbler is required, then it will be necessary to have them marked in some way.Bar coding is a common scheme used for this purpose.
In general, the larger the number of characteristics that can be evaluated, the more accurate is the object recognition. Size, shape, mass (or weight), light reflectivity, light transmittivity, texture, and temperature are examples of variable characteristics typical of everyday objects.