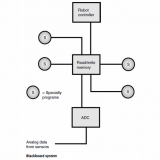
FLUXGATE MAGNETOMETER – 21054
A fluxgate magnetometer is a computerized robot guidance system that uses magnetic fields to derive position and orientation data. The device uses coils to sense changes in the geomagnetic field (Earth’s magnetic field), or in an artificially generated reference field.
Navigation within a defined area can be carried out by having the robot controller constantly analyze the orientation and intensity of the magnetic flux field generated by strategically placed electromagnets. A computer map of the flux field, showing two electromagnets and a hypothetical robot in the field, is shown in the illustration. In this case, opposite magnetic poles (north and south) face each other, giving the flux field a characteristic bar-magnet shape.
For each point in the work environment, the magnetic flux has a unique orientation and intensity. Therefore, there is a one-to-one cor- respondence between magnetic flux conditions and each point inside the environment. The robot controller is programmed to “know” this relation precisely for all points in the environment. This allows the robot to pinpoint its position in three-dimensional (3-D) space, provided a set of reference coordinates is established.